Lead poisoning is a critical health issue, particularly in children, due to their heightened vulnerability to its toxic effects. While prevention is paramount, effective treatment becomes essential when exposure occurs. Chelation therapy is a key treatment option, but its use is nuanced, depending on various factors such as blood lead levels (BLLs), symptoms, and specific scenarios like the presence of lead-containing materials in the gastrointestinal tract. This article delves into the intricacies of chelation therapy, providing a thorough understanding for an informative perspective.
What is Chelation Therapy?
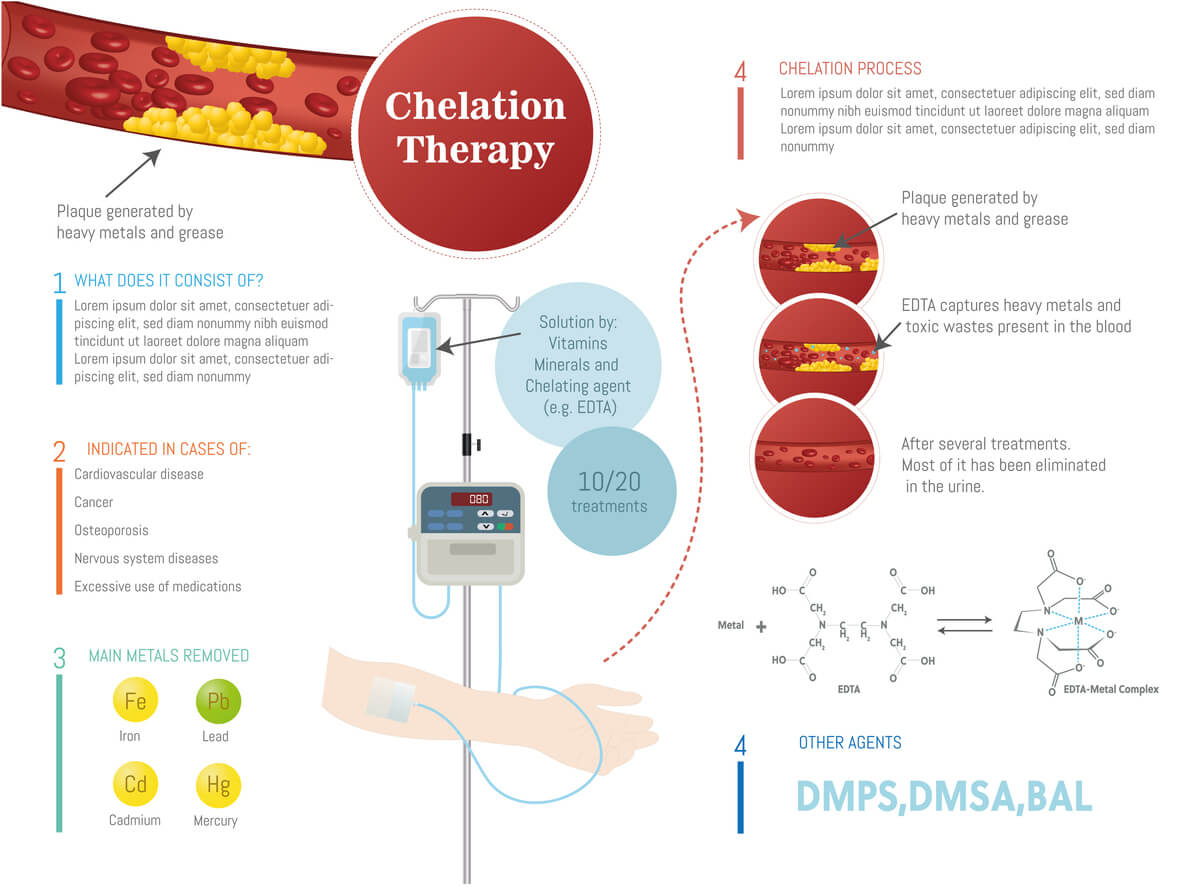
Chelation therapy involves administering agents like EDTA (ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid) that bind to lead in the bloodstream, facilitating its excretion, usually via the kidneys. While it’s effective in lowering lead levels, the therapy is not without risks, making its application in specific cases a subject of careful consideration.
Indications for Chelation Therapy
- Blood Lead Levels (BLLs): Typically, chelation is considered for children with BLLs over 45 µg/dL. However, these thresholds are dynamic, influenced by ongoing research and evolving guidelines.
- Symptomatic Lead Poisoning: Symptoms like abdominal pain, vomiting, and neurological disturbances may necessitate chelation at lower BLLs, addressing the immediate risks of lead toxicity.
- Radiographic Evidence of Lead in the Gastrointestinal Tract: In cases where imaging reveals the presence of lead objects, such as paint chips, in the stomach or intestines, chelation might be initiated to prevent further lead absorption, irrespective of current BLLs. The presence of radiographic signs of lead, such as paint chips in the colon or stomach, is a critical factor. Lead-containing materials in the gastrointestinal tract can lead to ongoing or acute lead exposure. In such scenarios, chelation therapy might be recommended even if BLLs are below the standard thresholds. This approach is aimed at reducing further absorption of lead and mitigating the risk of severe poisoning.
- Acute Lead Encephalopathy: This severe condition demands immediate chelation therapy, regardless of BLL.
- Chronic Exposure and Rising BLLs: Persistent high or rapidly increasing BLLs might require chelation to avert long-term health impacts.
- Pregnancy: For pregnant women with high BLLs, chelation is a complex decision due to fetal risk and is generally reserved for severe cases.
Risks and Side Effects
Chelation therapy can cause kidney damage, electrolyte imbalances, allergic reactions, and other side effects like nausea and low blood pressure. Monitoring and managing these risks under medical supervision is crucial.
Conclusion
Chelation therapy for lead poisoning is a decision that requires a nuanced approach, considering BLLs, symptoms, individual health factors, and specific scenarios like the presence of lead in the gastrointestinal tract. As research advances, guidelines for chelation therapy continue to evolve, emphasizing the need for informed decision-making and consultation with healthcare professionals.
This article aims to provide a detailed understanding but is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Always seek the guidance of healthcare providers for treatment decisions related to lead poisoning.
We welcome your legal questions for topically relevant articles in the future. Feel free to compose a question – it may be addressed in future articles. Email Question
Free Case Evaluation
Fill Out The Form Below To Find Out If You Have A Case.
Thank you for contacting us. One of our colleagues will get back to you shortly.